Healthcare is a primary concern the world over. The expectations from and the investments in the pharmaceutical industry globally are significant. The pharmaceutical industry's output impacts the quality of human lives and hence both opportunities and challenges are formidable. Research & Development (R&D) is at the core of the pharmaceutical industry's activities, be it product or process R&D. On a global scale, approx. 15 % - 19 % of revenues are spent on R&D and the expenditure is increasing each year. Yet, successful R&D is an elusive area and effort versus success is typically disproportionate. Drug discovery is a risky activity as an average of 5000-10000 lead compounds result in a single successful drug, which can cost in the region of US$ 250-500 million per drug.
Only 3 out of 10 new drugs generate enough revenue to match or exceed the average R&D spend of US$ 400 million per drug. Globally, R&D spends have grown at a higher rate than sales in recent years while NCE outputs have remained flat largely.
The number of new approved molecules has declined significantly and drug approval has become slower. FDA has taken a very cautious approach to new molecules reaching the market. The number of withdrawals has increased from a low of 2 in the 1980s to 13 in the last decade.
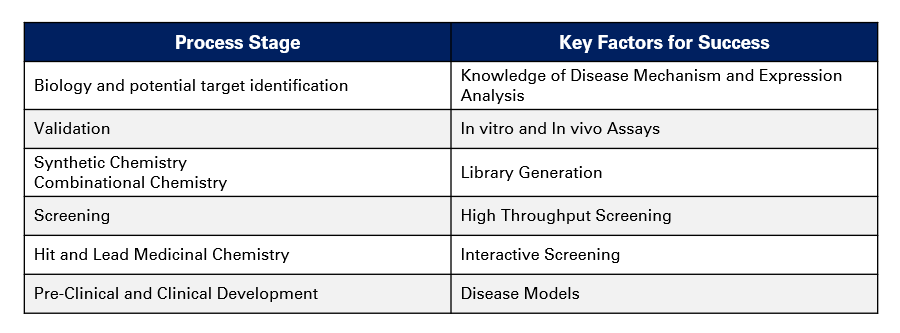
There are different factors at different stages of the drug discovery and development process that need to be considered in order to excel:
In the Indian scenario, R & D has always been a challenge. Spends at the industry levels are far lower than global standards at approx. 2-4% of revenues, with only the top 4-5 companies capable of spending more than 5% of revenues on R&D. This is further compounded by the fact that process patents allowed Indian pharmaceutical companies to reverse engineer, hence process R&D is a much stronger activity in India consequently lowering overall R&D spend requirements.
With imminent product patent laws, R&D in India is a whole new game. Irrespective of the growth and the opportunities in the global generic space that Indian pharmaceutical companies can exploit, there is an urgent need to evaluate the overall strategic issues of direction, investment and opportunity in the R & D space for the industry.
The key challenges facing the Indian pharmaceutical are:
Financial/Strategic
- Size of investment for successful drug discovery is significant with large risk.
- Choice of technology/approach NCE or biotech?, synthetic/ naturals/herbal?
- Defining revenue streams through licensing/partnership deals with ongoing investment in facilities, technology, recruitment, knowledge access, training, patent filing.
Customer
- Key therapy areas to be focused on, based on market being addressed and revenue opportunity being targeted.
- Mapping the pipeline against relevant disease areas.
- Overall cost of the final drug against investment in taking to market.
Process
- Access to market intelligence on competitor discovery activity/pipelines/ success & failure.
- Capabilities to select & monitor projects, manage patents filing, creating licensing deals.
- Capabilities in medicinal chemistry, molecular biology, pharmacology /pharmacokinetics, animal testing.
Organisation
- Skills and competencies in key areas such as molecular biology, pharmacokinetics are not easy to acquire and alignment of skills to focus therapy areas is a challenge.
- Retention of scientific staff is an area of constant challenge.
The R&D strategy needs to be defined based on an approach that allows for faster and profitable commercialisation. Clinical trials in India are being recognised now, with a number of international CROs already operational in the country through own/alliance operations. In fact, clinical research is predicted to be a key BPO area for the country. This essentially means that given the lower cost of R&D in India vs developed countries - at least 50-70% lower across the entire drug discovery and development process, there is an opportunity to implement a well defined R&D strategy going forward. The key areas that the overall R&D strategy needs to focus on are:
1. Identification of scientific capability on understanding the disease mechanism, the route (eg. synthetic vs naturals)
2.Identification of the key therapy areas for revenue opportunity based on markets being addressed and internal capability
3. Exploring partnerships in those therapy areas and manage parts of the discovery and development process internally and externally:
- Target identification & validation/selection
- Develope understanding of relevant disease mechanism
- Develope assays, screening & lead molecule identification
- Patent filing process data generation, analysis, overall development of patent
- Limited clinical trials eg. upto phase 2a; proof of concept in humans
Creating licensing deals or the joint ventureIt needs to be recognized that R&D strategy should dovetail the business strategy of the organisation from all perspectives so that R&D is not seen as an investment with low returns. Hence, just as one would detail the business strategy with an emphasis on financial and non financial linkages in order to create an implementable framework, so also R&D strategy needs detailing.
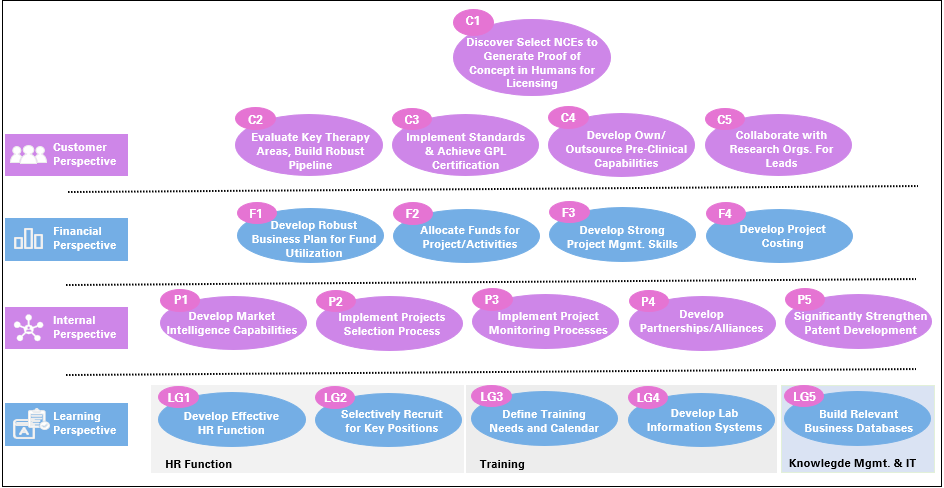
Using the Strategy Map approach of the Balanced Scorecard framework, a well articulated R&D strategy would address customer (expectations from R&D by the corporate), financial, process and organizational issues and lay out a roadmap for focused implementation.
In summary, a robust R&D strategy would address the following themes:
- Enhancement of the discovery & development process that leads to rapid commercialisation.
- Development of relevant pre-clinical and clinical capabilities.
- Active collaboration with partners for long-term sustainability.
- Efficient allocation and utilisation of funds.
- Tracking market intelligence and upgradation of lab and computing facilities.
- Building an HR function for motivation and retention of scientific staff.
- Build suitable knowledge bases to facilitate business delivery
To read more such insights from our leaders, subscribe to Cedar FinTech Monthly View